WHAT IS THE MEANING OF A CELL
DEFINITION: The cell is defined as the structural and fictional unit of a living organism . it is also the simplest, the smallest and basic unit of life.
All living things, plants and animal are made up of cells. The cell is regarded as the basic unit of all living things because it can carry out all life activities such as feeding, reproduction, excretion, growth, adaptation, respiration , sensitivity and movement. etc.
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM
Living organism are classified into two major groups, which are;
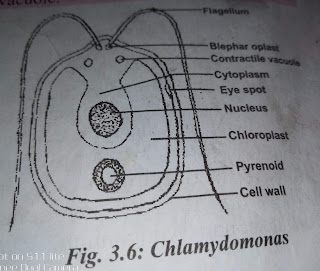
(a).UNICELLULAR ORGANISM: Unicellular organism are organisms that consist of only one cell. examples are Chlamydomonas, Euglena, Amoeba, Paramecium.
(b). MULTICELLULAR ORGANISM: These are organisms which consist of two or more cells. or they have multiple cells. examples of multicellular organism are Hydra, Spirogyra, Volvox, flowering plants and man.
THEORY OF THE CELL
The cell theory state that
1. The cell is the structural and fictional unit of life.
2. All living OK organisms are made of cells.
3.All cells come from previously existing cells.
4. There is no life apart from the life of cell.
5. All living things are either single cells or group of cells.
FORMS IN WHICH CELLS EXISTS
There are four forms in which cell exists, these are
(a). AS A COLONY:
some organisms are made of many similar cells which are joined together but they cannot be differentiated from each other.
Therefore the compilation of independent cells or protists is called a colony. examples of organisms that exists as colony are Pandorina, Volvox and sponges.
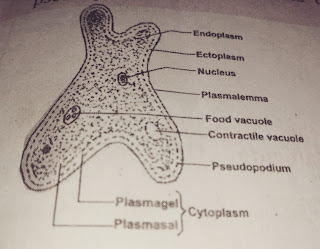
(b). AS INDEPENDENT OR FREE LIVING ORGANISM: independent or free living organism are organisms that are capable living on their own freely and posses only one type of cell and each cell can carry out all the life processes such as feeding, movement, reproduction, etc. examples are Amoeba, Euglena, Paramecium, chamydomonas etc.
AMOEBA: Amoeba has a rough shape, and can change it shape at any time. the protoplasm is made up of nucleus and cytoplasm . the food and contractile vacuole are embedded in the cytoplasm. it uses pseudopdia for movement.
PARAMECIUM: Paramecium is best known for having a slippers shape. the cytoplasm is made up of ectoplasm and endoplasm. it has two nucleus, micro and. mega nucleus. what houses the food vacuole cyot_stome, is the Cytoplasm. The organ for movement is Cilia.
CHLAMYDOMONAS: chlamydomonas is a free mico organism or plant that is unicellular in nature. it has an eye spot, chloroplast, food vacuole, and contractile vacuole. it organ for movement is Flagella.
EUGLENA VIRIDIS: Thus is a protist and a typical example of an organism having the characteristics of both plants and animal. it possess gullets, flagellum, contractile vacuole, pellicles, myonemes, eyespot, pyrenoids etc. euglena moves with the aid of flagellum.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLANTS AND ANIMAL CELLS
1.plant cell has chloroplast while animal cell has no chloroplast.
2. it is usually rectangular and definite in shape while the animal cell is spherical and indefinite in shape.
3. plant cell has a rigid cell wall while animal cell has no cell wall.
4. plant cell has no flexible cell membrane while animal cell membrane is flexible
5.plant cell has large vacuole while animal cell has small vacuole
6. plants cell stores lipid as oil while animal cell stores lipid as fat.
7.plant cell has no centriole while animal cell has centriole.
TERMINOLOGIES APPLICABLE TO A CELL
1.NUCLEUS
The nucleus has a spherical body which contains hereditary materials. genes and chromosomes are located at the center of the cell, which is embedded in the cytoplasm.
2. CHROMOSOMES
Chromosomes are located in the nucleus and they contains deoxyribonucleic acid DNA.
3.MITOCHONDRIA
The mitochondria is the power house of the cell. they are respiratory sites where energy is released from simple sugar.
4. VACUOLE
It contains cell sap which act as an Osmoregulator by helping to remove excess water in cells.
5.NUCLEOLUS
These are dense structure within the nucleus that produce ribosomes for protein synthesis .
6.ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
They are membrane like structure that forms channel within the cytoplasm. they aid the transport of materials within the cytoplasm.
7.GOLGI BODIES
These are series of disc shaped sacs. They function in synthesis, packaging and distribution of materials.
8.CHLOROPLAST
These are large green organels in plants cells. they contain chlorophyll which aid photosynthesis.
9. LYSOSOMES
These are thin wall bodies and they contain enzymes. They are sites for respiratory enzymes.
10. RIBOSOMES
These are small round bodies attached to endoplasmic reticulum. They are responsible for protein synthesis.
11.CELL WALL
It is a tough , fairly rigid structure that is freely permeable in plants cells. It provides shape, and mechanical support for the cell.
12.CELL MEMBRANE
This is a flexible membrane made up of mainly proteins and lipids . it is selectively permeable and it also help in selective reabsorption.
13.CENTRIOLES
Three are two small granules near nucleus of animal cells from which flagella or cilia emerge.
14. STARCH GRANULES
These are oval or round structures mostly found in plant cells. they stores starch.
Euglena viridis
Plant cell

Animal cell

CHECK OUT MY TOP LISTED POSTS
other posts are




Comments
Post a Comment